Last modified: May 21, 2025
Caching
-
Saving the results of a calculation or request so that in the future, those results can be reused instead of redoing the calculation or request
- Caching is often the best first step to make your site faster and able to handle more users
-
Benefits: Makes calculations or requests run faster (or skips them entirely)
-
Risks: The results you saved may be out of date (stale)
-
Also, some requests can’t be cached for different reasons:
-
The response may be unique each time (e.g., generate a random number)
-
You want the server to perform an action (e.g., POST or DELETE requests)
-
You always want most up to date (e.g., bank account balance)
-
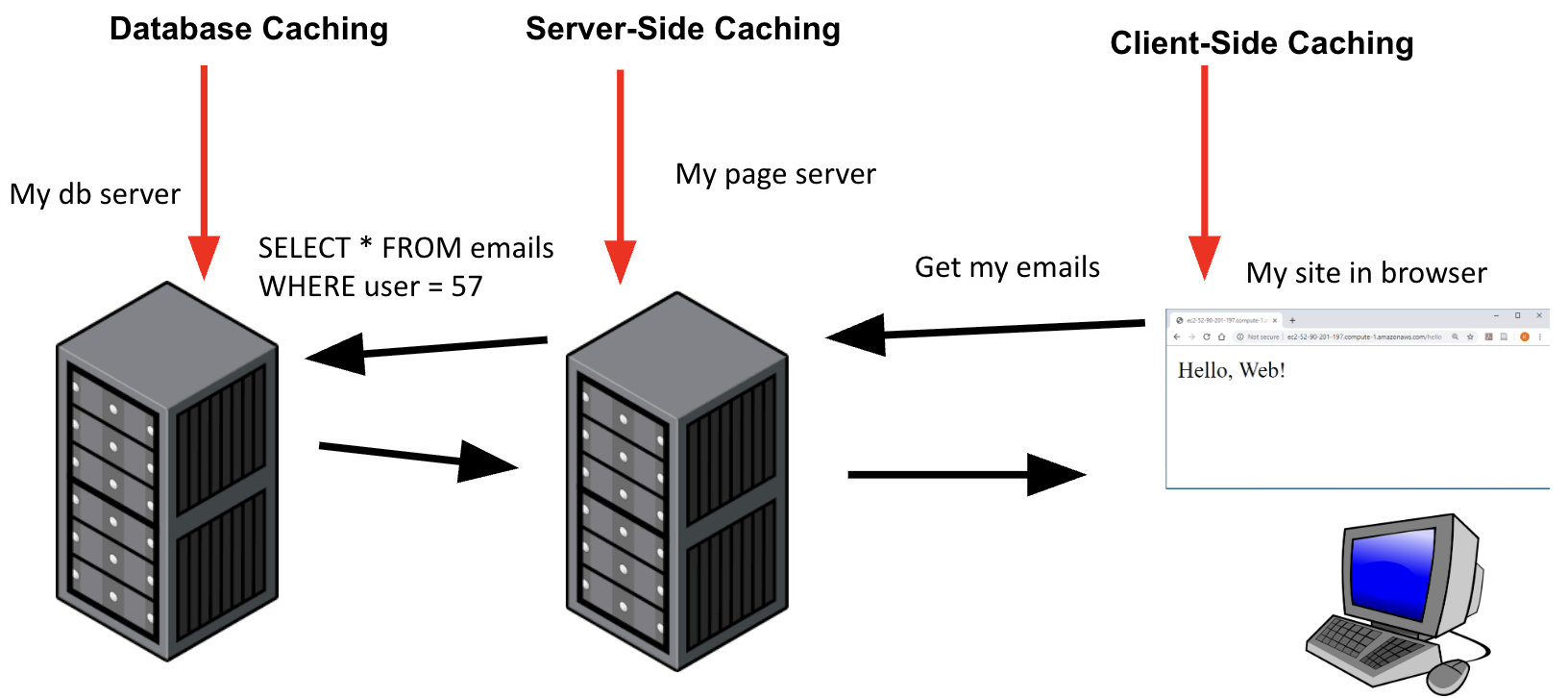
Caching locations
app.js
import express from 'express';
import path from 'path';
import cookieParser from 'cookie-parser';
import logger from 'morgan';
import sessions from 'express-session';
// This is a public sample test API key.
// Don’t submit any personally identifiable information in requests made with this key.
// Sign in to see your own test API key embedded in code samples.
import stripeLib from 'stripe'
const stripe = stripeLib(' ');
import models from './models.js'
import itemsRouter from './routes/items.js';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
import { dirname } from 'path';
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
const __dirname = dirname(__filename);
var app = express();
app.use(logger('dev'));
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use(cookieParser());
const oneDay = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24;
app.use(sessions({
secret: "thisismysecrctekey",
saveUninitialized:true,
cookie: { maxAge: oneDay },
resave: false
}))
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
app.use((req, res, next) =>{
req.models = models
req.stripe = stripe
next()
})
app.use('/items', itemsRouter);
export default app;
items.js
import cache from 'memory-cache'
import express from 'express';
var router = express.Router();
// artificially slow down the response
async function getItemsSlow(req) {
const allItems = await req.models.Item.find()
const sleepSeconds = 5
await new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, sleepSeconds * 1000))
return allItems
}
router.get("/", async (req, res) => {
console.log("got a GET request for all items, first check the cache")
let allItems = cache.get("allItems")
if (allItems) {
console.log("cache hit: found items in my cache")
}
else {
console.log("cache miss: doing the slow db lookup")
// let allItems = await req.models.Item.find()
allItems = await getItemsSlow(req);
console.log("loaded items from db, saving to cache")
cache.put("allItems", allItems, 30 * 1000)
}
// res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=30')
res.json(allItems)
})
router.post("/saveCart", async (req, res) => {
console.log(
"saving card, session is currently: ",
req.session
)
const cartInfo = req.body
//TODO: validate cart info is only item ids and counts
// for some reason if I save an object (instead of string)
// it gets deleted later
req.session.cartInfo = JSON.stringify(cartInfo)
console.log("session is now", req.session)
res.json({status: "success"})
})
router.get('/getCart', async (req, res) => {
if(!req.session || !req.session.cartInfo){
// if no session or saved cart, just return empty cart
res.json([])
return
}
const cartInfo = JSON.parse(req.session.cartInfo)
// add item names and prices to the cart info
const combinedCartInfo = await addPricesToCart(cartInfo, req.models)
res.json(combinedCartInfo)
})
async function addPricesToCart(cartInfo, models){
//cartInfo should start like: [{itemId: 342, itemCount: 2}, {itemId:345, itemCount: 1}, ...]
// look up in the db all the items listed in my cart
const cartItemIds = cartInfo.map(cartItem => cartItem.itemId)
const itemsInfo = await models.Item.find().where("_id").in(cartItemIds).exec()
// itemsInfo will be an array of json, like this:
// [{_id:342, name: "orange", price: ...}, {_id: 345, name: "apple", ...},...]
// transform itemsInfo into an object where I can look up info by the id
let itemsInfoById = {}
itemsInfo.forEach(itemInfo => {
itemsInfoById[itemInfo._id] = itemInfo
})
// itemsInfoById will look like
// {
// 342: {_id:342, name: "orange", price: ...}
// 345: {_id: 345, name: "apple", ...}
// }
// take the cartInfo, and for each item, make a new object that includes the name and price
const combinedCartInfo = cartInfo.map(cartItem => {
return {
itemId: cartItem.itemId, // from user cart
itemCount: cartItem.itemCount, // from user cart
name: itemsInfoById[cartItem.itemId].name, // from the db
price: itemsInfoById[cartItem.itemId].price // from the db
}
})
return combinedCartInfo
}
async function calculateOrderAmount(req){
// get cart info, combine with prices, calculate the total price
const cartInfo = JSON.parse(req.session.cartInfo)
const combinedCartInfo = await addPricesToCart(cartInfo, req.models)
const totalCost = combinedCartInfo
.map(item => item.price * item.itemCount) // get cost for each item type
.reduce((prev, curr) => prev + curr)
return totalCost
}
router.post('/create-payment-intent', async (req, res) => {
//look up the order amount
let orderAmount = await calculateOrderAmount(req)
// create a PaymentIntent object with the order amount
const paymentIntent = await req.stripe.paymentIntents.create({
amount: orderAmount * 100,
currency: "usd", // note: 'usd' is actually US cents for some reason (US dollars * 100)
automatic_payment_methods: {
enabled: true
}
})
res.send({
clientSecret: paymentIntent.client_secret
})
})
export default router;