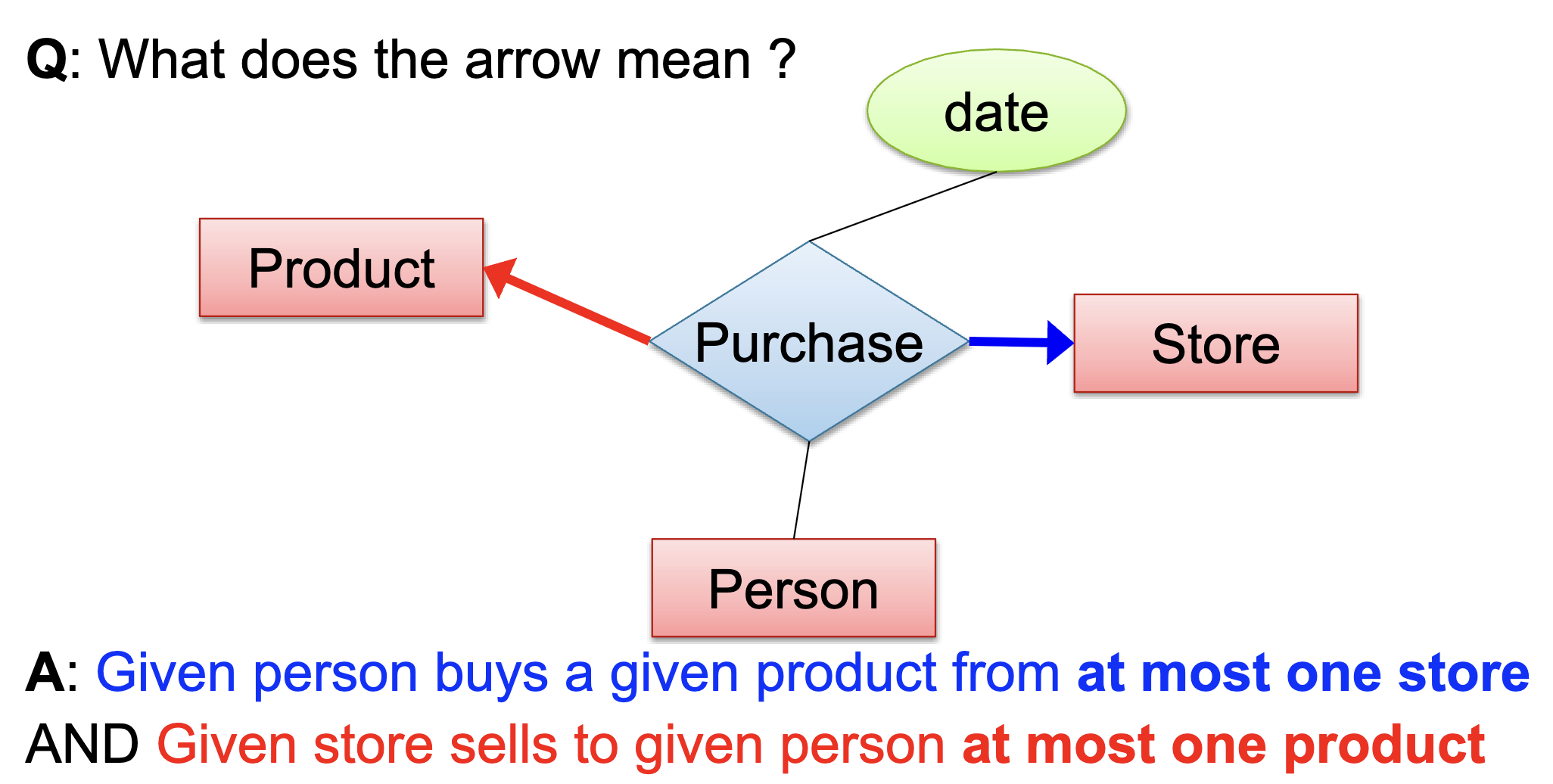
Last modified: May 24, 2025
Relationship
If A and B are sets, then a relation R is a subset of A * B
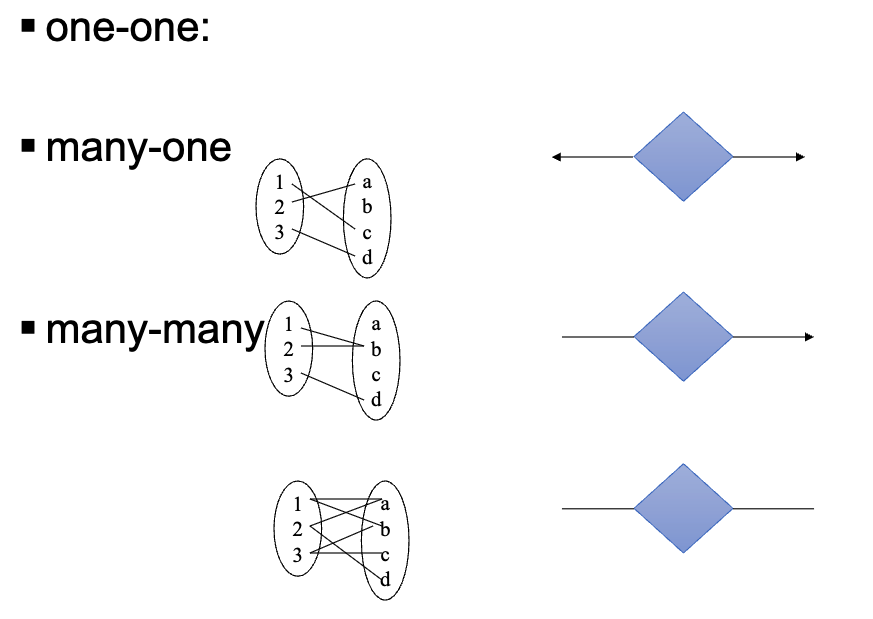
- One-to-one
- One-to-many; Many-to-one
- Many-to-many

Multiplicity & Cardinality
- In UML, multiplicity specifies lower and upper bound constraints on the cardinality of a relationship
| Multiplicity | Cardinality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0..0 | 0 | Collection must be empty |
| 0..1 | Either zero or one instance | |
| 1..1 | 1 | Exactly one instance |
| 0..* | * | Zero or more instances |
| 1..* | One or more instance | |
| 5..5 | 5 | Exactly 5 instances |
| m..n | At least m, but no more than n instances |
Multi-way Relationships
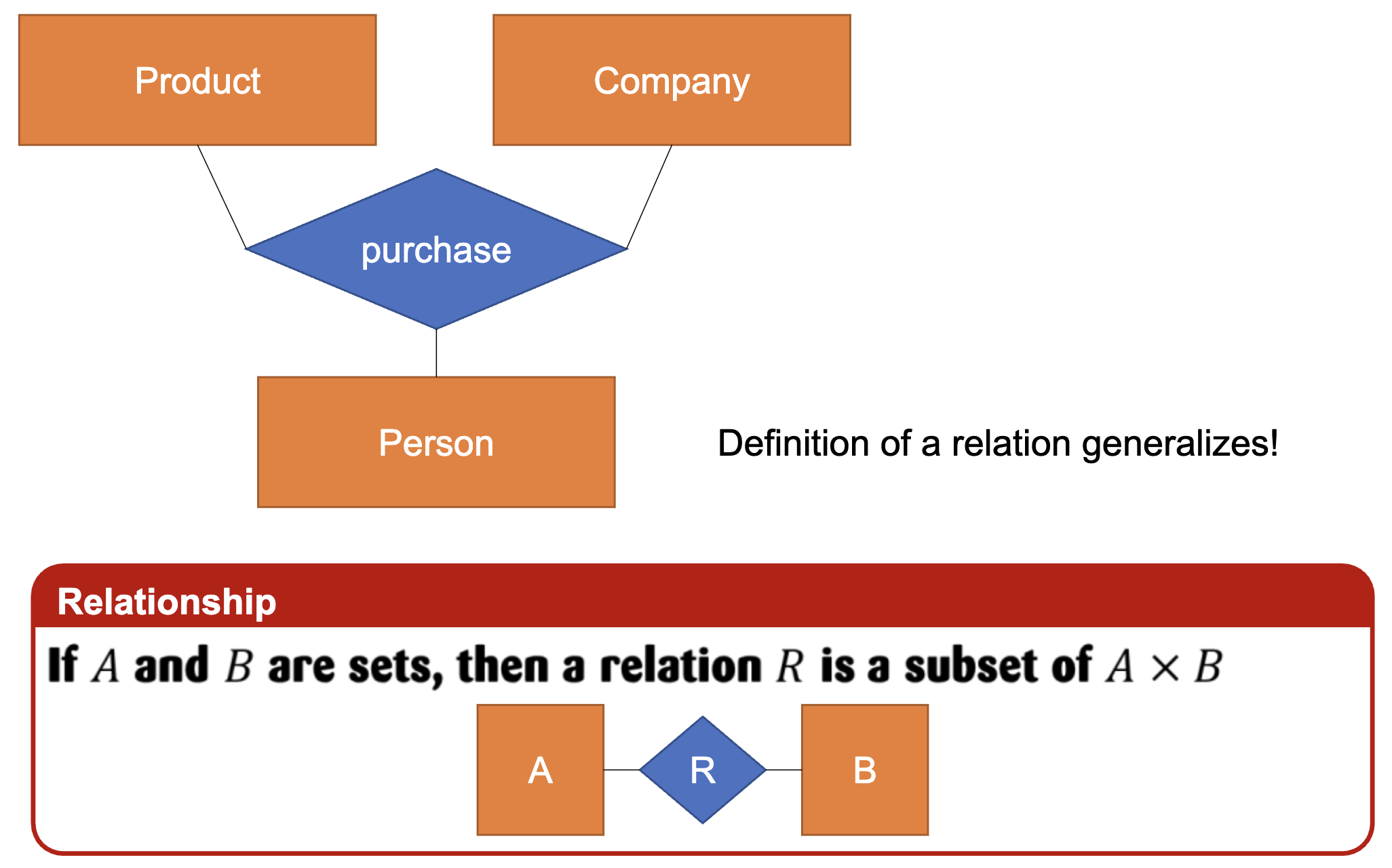
A and B are two sets (collections of things).
Example:
A = {Person1, Person2}
B = {Product1, Product2}
A × B (called the "Cartesian product") is all possible combinations of one item from A and one item from B.
A × B = { (Person1, Product1), (Person1, Product2), (Person2, Product1), (Person2, Product2) }
Relation R is some subset of A × B — meaning R just picks certain pairs out of A × B that actually make sense for the relationship you're modeling.